Decentralized ecosystems in relation to creative industries
Let’s discuss how decentralized ecosystems can transform creative industries, like the one we’re a part of!
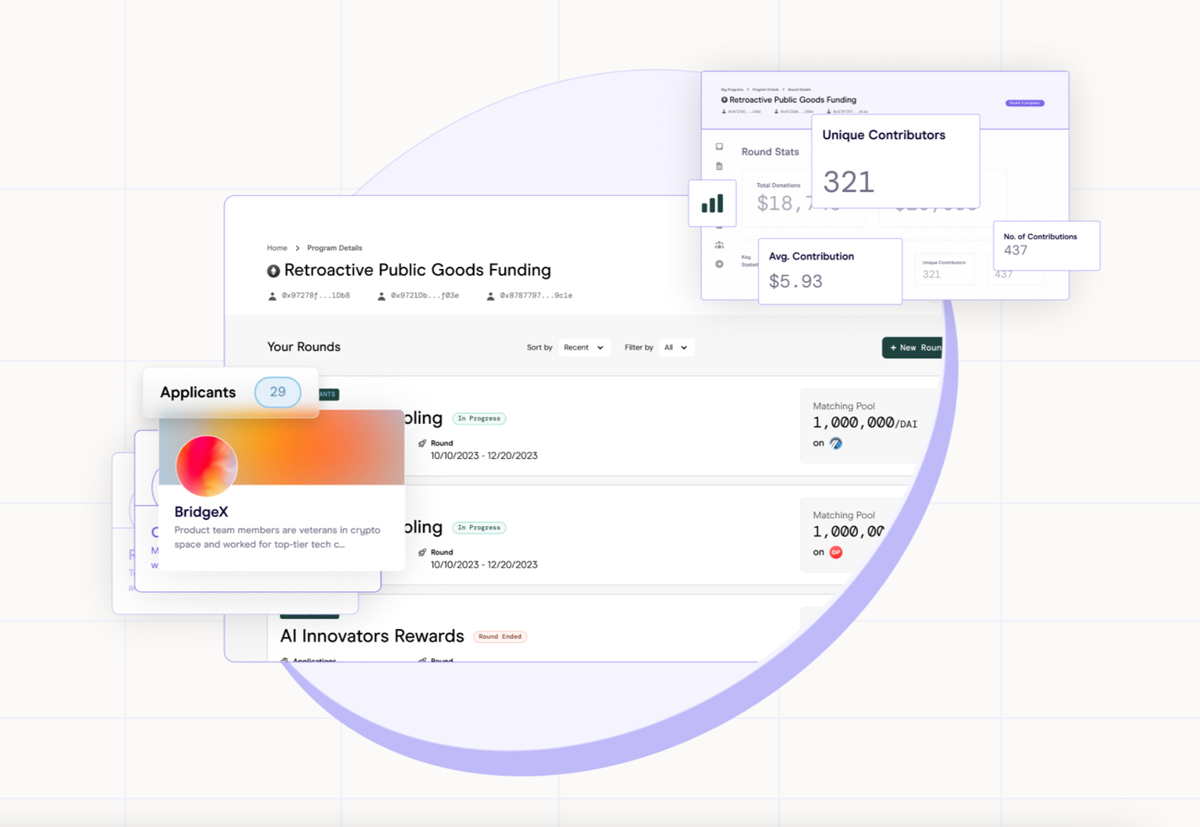
Recently, we’ve had the incredible opportunity to be part of the second community funding round in Octant, a platform typically focused on developers. As contributors to The ALANA project, we were introduced to Octant and its open call for marketing community projects. We were chosen to create educational content in our own language and style to introduce Octant to people like us in the creative industry.

Our goal is to help others understand the importance of supporting platforms like Octant, which fund open-source and public good projects.
As one of the articles from Wonderloot puts it:
“The goal of Web3, as I understand it, is to leverage blockchain technology to produce a sustainable digital economy for all creators, builders, and knowledge workers.
A better Internet, one not ruled by advertising revenue and the perverse algorithmic incentives that arise as a result. An Internet that preserves the value of human creativity, especially in the Age of AI.”
This vision is what drives us toward the future of decentralised creative ecosystems.
Today’s Challenges in the (mostly) Centralized Creative Industries
The centralized nature of traditional creative industries has led to several challenges:
- Inequitable Pay Structures
Many creators, especially those starting out, receive only a small fraction of the profits their work generates, with the bulk of the earnings going to intermediaries or large corporations. For example, Spotify pays artists a fraction of a cent per stream, with most of the revenue going to the platform and record labels. Independent musicians struggle to sustain themselves, even with significant traction. - Limited Access for Emerging Artists
In centralized systems, established brands dominate the market, making it difficult for new and independent designers to gain visibility. A clear example of this is Amazon’s dominance in e-commerce, where smaller designers and brands face challenges competing. Often, Amazon’s in-house brands, like Amazon Basics, are prioritized over independent products, making visibility an uphill battle. - Lack of Inclusivity
Centralized industries can perpetuate biases, overlooking marginalized voices and underrepresented communities. For instance, high-profile events like Fashion Week have often lacked diversity, with limited representation of Black, Indigenous, and Plus-Size designers and models. This results in a narrow perspective dominating mainstream fashion narratives until trends shift momentarily, only for everything to revert back. - Lack of Transparency
Centralized industries often operate behind closed doors, with little insight into production processes or sourcing practices. Brands like Shein and H&M have faced criticism for opaque supply chains, where consumers often don’t know the origins of their clothing, and ethical concerns arise due to exploitative labor practices. (and unfortunately, we don’t see this behavior only in fast fashion brands) - Shared Data and Content on Social-Media
Creators frequently rely on social media platforms to reach audiences, but these platforms are controlled by centralized entities that disproportionately benefit from user-generated content. This leaves creators struggling to maintain ownership of their work and receive adequate compensation. For example, the recent temporary TikTok ban in some regions left many businesses and creators powerless, as they lost access to their audience and content without recourse.
These challenges underscore the urgent need for decentralized ecosystems that prioritize fairness, inclusivity, and community support. By addressing the shortcomings of centralized systems, decentralized ecosystems can bring much-needed innovation and inclusivity to creative industries.
How Creators Can Benefit from Open-Source Tools and Public Goods
The rise of open-source tools and public goods provides creators with transformative opportunities to overcome the barriers posed by centralized systems and high costs.
Here’s how:
- Cost-Effective Access to Tools
Open-source software offers free or low-cost alternatives to expensive proprietary tools, helping creators save money and reduce financial strain.
For example:
- GIMP and Inkscape offer powerful alternatives to Adobe Photoshop and Illustrator.
- Blender, a leading open-source 3D modeling, animation, and rendering software, rivals expensive tools like Autodesk Maya.
- Audacity and Ardour provide creators with open-source audio production tools at no cost.
The cost of proprietary software can be overwhelming.
For example:
- Adobe Creative Cloud costs $54.99/month ($659.88/year).
- Autodesk Maya costs $225/month ($1,785/year).
These subscription fees can be more than the cost of living, adding an unnecessary burden to us as creators who are already juggling essential expenses like rent and food. Imagine the creative potential that could be unlocked if creators didn’t have to worry about these costs, allowing them to focus on their craft and innovation.
- Ownership and Creative Freedom
Open-source tools grant creators full ownership and control over their work. Unlike proprietary platforms that can limit access or impose restrictions, open-source software provides boundless creative freedom.
- WordPress enables creators to build and control their websites, avoiding dependence on centralized services.
- Tools like Blender and GIMP offer high customizability, ensuring creators can tailor their workflows to meet their specific needs and encourage innovation.
- Unlock Protocol provides creators with free, user-friendly smart contracts to monetize their content not only through minting digital assets, but also memberships and subscriptions. It empowers creators to manage access and revenue directly, without intermediaries, offering a simple and accessible way to build sustainable creative businesses.
- Community Support and Collaboration
Open-source communities foster collaboration, support, and the sharing of resources. Creators can engage with others, access assistance, and contribute to collective innovation.
- GitHub facilitates global collaboration on open-source projects, and platforms like Gitcoin integrate with it for authentication and project management, focusing on decentralized, blockchain-based project funding and development.
- Blender’s vibrant community constantly contributes tutorials, plugins, and feedback to improve the tool.
- Farcaster, Zora, and Rodeo.club are decentralized social networking platforms that empower creators to own their identity, share their work, and collaborate freely, without centralized gatekeepers.
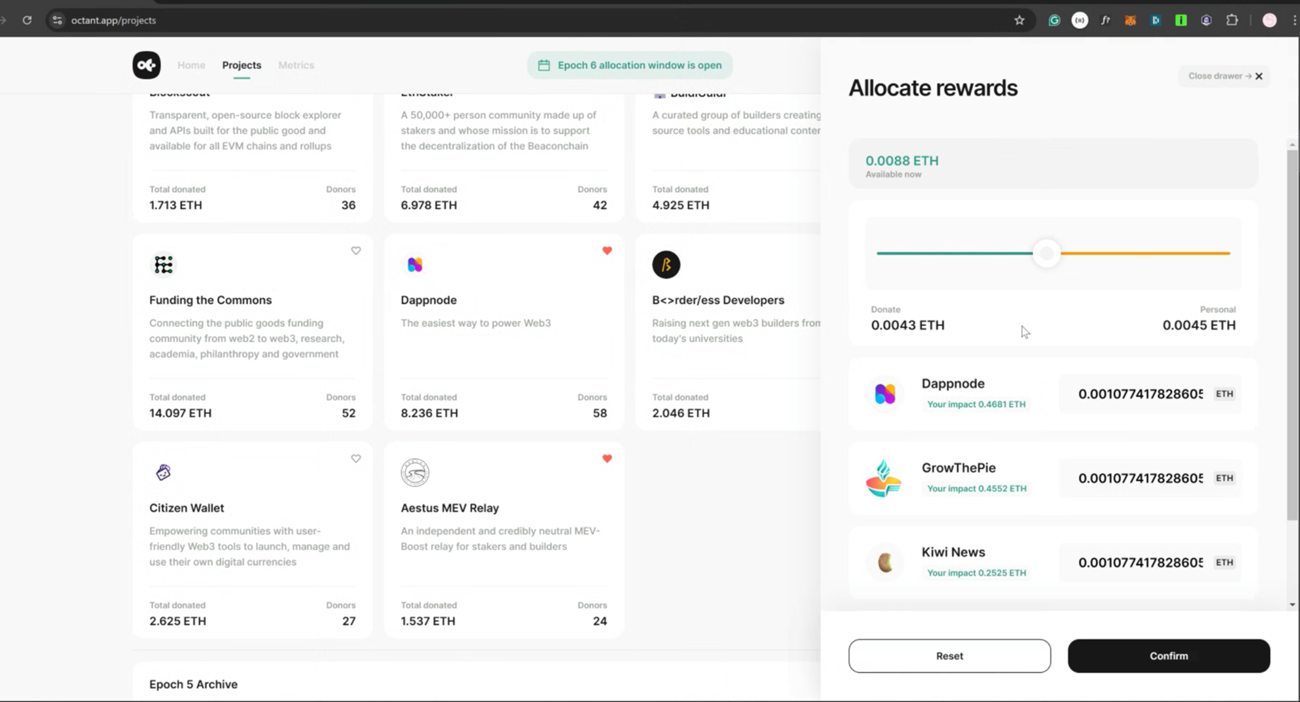
Supporting these communities amplifies their ability to grow and deliver impactful tools. Platforms like Octant exemplify this by offering funding and support for open-source tools and public good projects. By backing such platforms, we can ensure a vibrant ecosystem that benefits everyone, from creators to engineers, shaping a better future.
- Access to Public Goods
Open-source resources, such as Creative Commons-licensed content and public datasets, provide invaluable resources for creators.
- Creative Commons licenses allow creators to freely incorporate images, videos, and music into their projects.
- Blender’s Asset Library offers free, community-generated 3D models and textures.
- Open Data Portals, like those from the World Bank or NASA, give creators access to valuable datasets for visualizations and applications.
5. Decentralized Distribution and Funding
Blockchain-based platforms and public goods projects help creators bypass traditional gatekeepers, enabling more equitable compensation and distribution.
- NFT marketplaces allow creators to sell their digital work directly to buyers, ensuring fair compensation.
- Peer-to-peer platforms like IPFS enable decentralized hosting and sharing of work.
Crowdfunding platforms like OpenCollective and Gitcoin Grants provide community-driven funding for creative and open-source projects, ensuring sustainable income streams for creators.
Why Support Open-Source Communities?
Supporting platforms and communities that back open-source software is vital for the sustainability and growth of creative industries. By contributing to or funding open-source and public good projects through platforms like Octant, creators and organisations help keep these essential tools accessible and continuously improving. For instance, industries like fashion or jewelry can draw from Octant’s approach to create more sustainable ecosystems and apply similar frameworks to drive future innovation.
Leveraging open-source tools and public goods enables creators to focus on what really matters: creativity, problem-solving, and innovation. By supporting these tools and their communities, we collectively invest in a more inclusive, equitable, and sustainable future for creators worldwide. This support empowers creators to push the boundaries of their craft, knowing that the tools they rely on are not only accessible but continually improving for the benefit of the entire creative ecosystem.
We are going to share more information about Octant in detail and some of the tools we are using in our next articles. So stay tuned!
Sources
- Centralized and Decentralized Ecosystems: https://visionspol.eu/en/2021/12/07/centralized-and-decentralized-ecosystems-what-are-the-differences/
- Octant Documentation: https://octant.app/?mtm_campaign=community-fund&mtm_kwd=orbyline
- Recalibrating: https://wanderloots.com/recalibrating-52/
- The Alana Project: https://mirror.xyz/the-alana-project.eth/
- GitHub: https://github.com/pricing
- Gitcoin: https://www.gitcoin.co/