The Evolution of Additive Manufacturing Jewelry
Market Trends and Projections for the next 10 years
The world of jewelry is going through a significant change, made possible by the fast progress in 3D printing and AM technology. When we turn our eyes to the future, the market for jewelry created with AM shows great promise of growth due to inventive methods in manufacturing and shifts seen among consumers.
This worldwide sector is projected to expand considerably in the coming decade, as per recent market analysis. This rise can be attributed to a variety of reasons such as growing requests for personalization, lessened production expenses and the capacity to make complex designs which were not possible before through conventional making processes.
You can check out our article about the differences between 3D Printing and Additive manufacturing to understand better why we don’t use 3D Printing term everywhere.
Key Technologies Shaping the Market
The Additive Manufacturing jewelry landscape is dominated by several cutting-edge technologies:
- Stereolithography (SLA): This method is famous for its accuracy and fine surface quality, making it excellent in producing detailed models of jewelry.
- Select Laser Sintering (SLS): Can handle various materials, including metals, so it is good for creating jewelry that is ready to be used at the end.
- Digital Light Processing (DLP): This method is faster in printing and is used for making smaller parts with detailed designs.
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): This method is not so usual for jewelry, but it can be very good in making prototypes and molds that are not too costly.
- Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS): This is a more recent technology that has been getting attention for its capacity to produce intricate metal jewelry straight away.
Market Applications and Trends
The Additive Manufacturing jewelry market caters to various applications:
- Prototyping: Allowing designers to quickly iterate and refine their concepts before mass production.
- Custom Jewelry Creation: Enabling personalised designs tailored to individual customer preferences.
- Limited Edition Collections: Facilitating the production of unique, small-batch jewelry series.
- Restoration and Reproduction: Assisting in the recreation of old or broken items with great precision.
The market is experiencing an increasing demand for sustainable and environmentally-friendly jewelry production. 3D printing & AM help meet this need because it reduces material waste and allows for the use of recycled substances in creating these products. This technology is being used more often in the making of fine jewelry as luxury brands are trying out its possible use for producing high-end pieces.
Industry Leaders and Innovators
While established companies still dominate the market, innovative newcomers are disrupting the industry with fresh approaches:
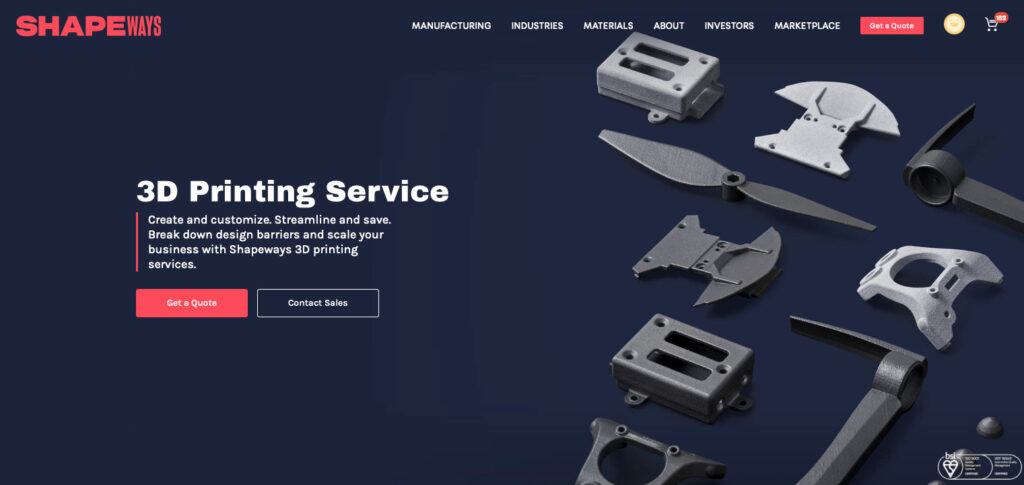
- Shapeways: Pioneers in on-demand additive manufacturing (AM) and 3D printing services. They offer a marketplace where designers can create and sell 3D-printed jewelry. Shapeways has printed over 21 million parts since its founding in 2007 and works with a wide range of materials including precious metals.
- DWS (Digital Wax Systems): An Italian company specializing in high-precision stereolithography (SLA) printers and proprietary resins for jewelry production. Their XFAB series is particularly popular among jewelers for its ability to print highly detailed wax models for casting.
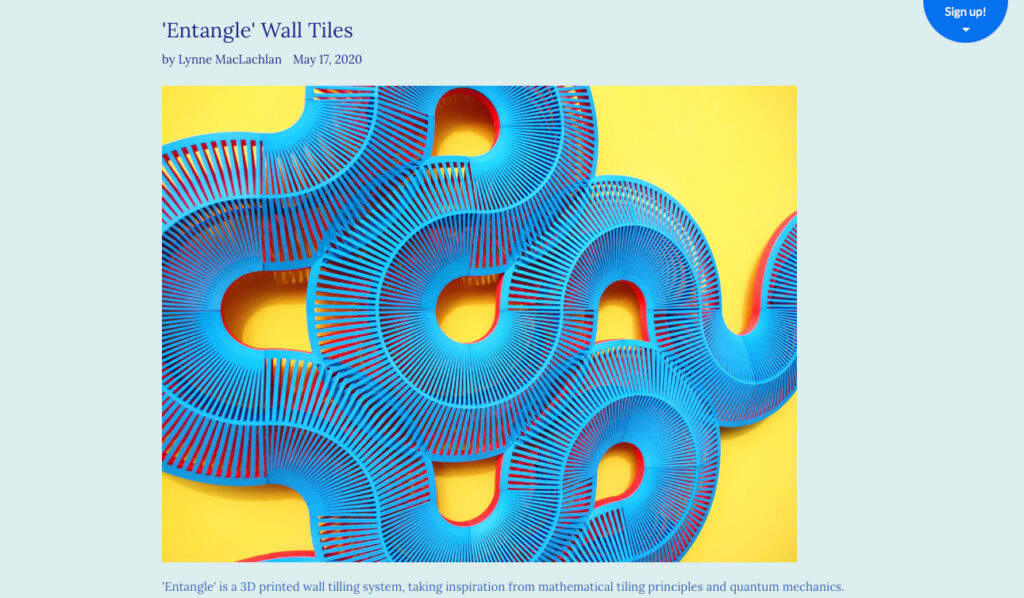
Lynne MacLachlan: A Scottish designer known for her colorful, geometric jewelry designs. MacLachlan’s work has been presented at the prestigious Victoria & Albert Museum in London. She uses parametric design software to create complex, intricate structures that are then 3D printed. Her “Geometric” collection, featuring bold, interlocking shapes, has become her signature style.
Maison 203: An Italian design company founded in 2011, specializing in AM and 3D printed jewelry and accessories. Their strong point is collaboration with other designers to create unique designs. They’ve worked with notable designers like Odo Fioravanti, Monica Castiglioni, Arturo Tedesch, Giulio Iacchetti and many more.
Nobahar Design Milano: After studying Additive Manufacturing techniques and working in the industry since 2013, multidisciplinary designer Sogand Nobahar founded her 3D objects brand in Milan in 2017. The brand primarily uses Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) technology, combining traditional production processes and coloration with modern techniques. All pieces are conceptual, with strong narratives. She has won several prizes, and her work has been featured on fashion runways in Milan, Paris, and Berlin.
Eve Balashova: She combines 3D printing with traditional metalworking techniques to create unique, and sometimes large-scale pieces. Using 3D printed nylon, she crafts bold, colorful, and lightweight jewellery inspired by geometric and natural motifs. Each piece features smooth, hand-dyed color transitions and is complemented by handcrafted precious metal elements.
Nervous System: Famous for their algorithm-based designs in 3D printed jewelry. Founded by Jessica Rosenkrantz and Jesse Louis-Rosenberg, they use computational design to create complex, organic forms. Their “Kinematics” dress, a 3D printed garment that unfolds into shape when removed from the printer
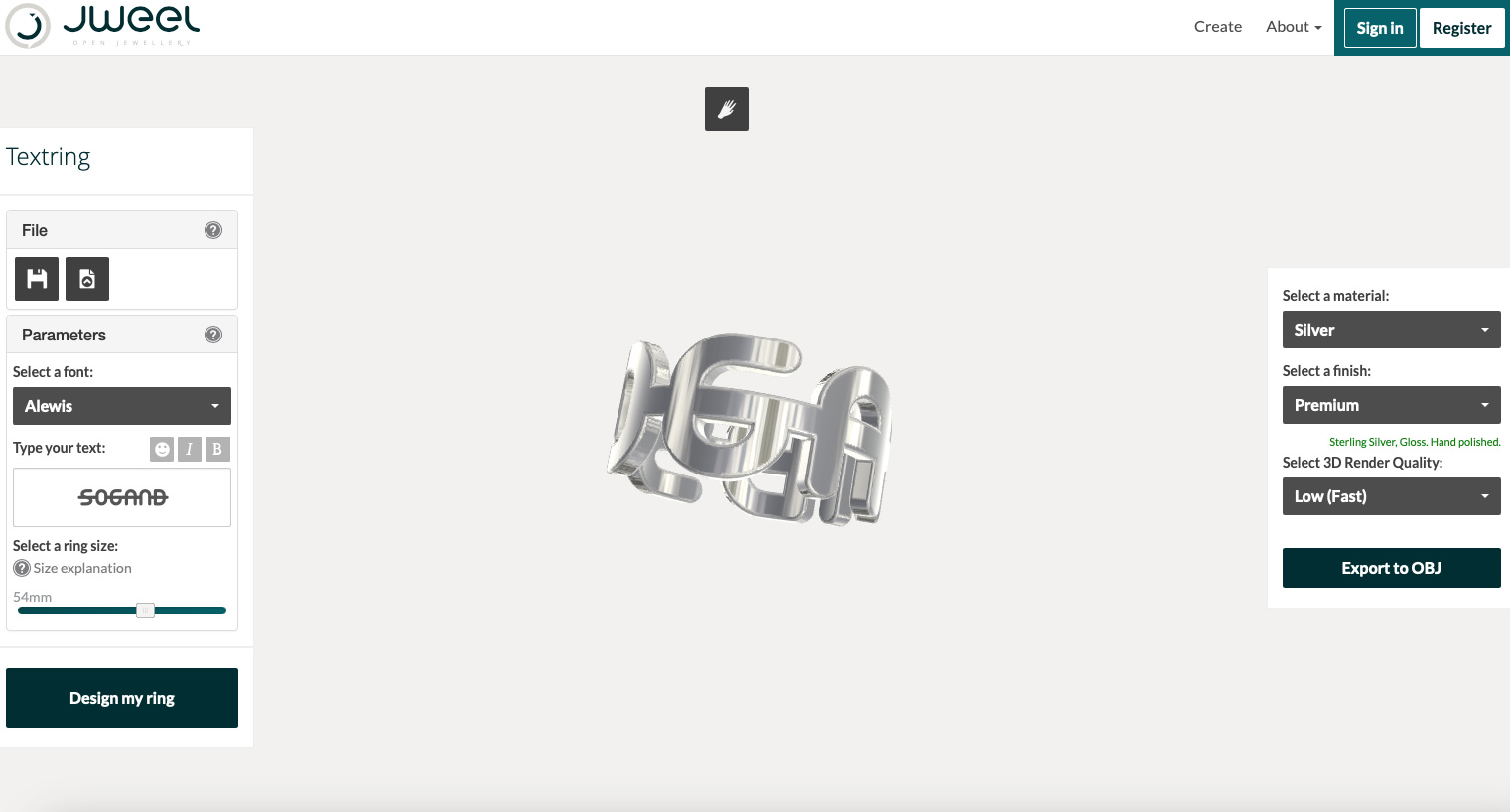
Jweel: A digital service allowing customers to create unique jewelry designs using easy-to-use tools, which are then 3D printed. They offer a range of materials including sterling silver, gold-plated brass, and stainless steel. Jweel’s platform has been used to create over 100,000 custom designs since its launch.
These are some of the innovators that are reshaping the jewelry and accessories industry by leveraging 3D printing technologies to create unique, customizable, and complex designs that were previously impossible or impractical to produce using traditional manufacturing methods.
Market Challenges and Opportunities
Although the future seems bright for the AM jewelry market, it encounters challenges too. Some of these include limitations in materials that can be used to create jewelry pieces, requirements for post-processing after printing is completed and demand for experts in designing who are skilled with 3D modeling software. Nevertheless, these difficulties may also offer chances to innovate and specialize within this sector.
3D printing and AM technologies is getting better all the time. We might see increased speed in printing, improvements in material properties and finish quality. This could cause more use of laser and 3D printing across various jewelry sections like costume or high-end luxury items.
Looking Ahead
The future for AM jewelry is shining, with predictions of major market growth by the next 10 years. As these processes becomes easier to use and better in quality, it could change the way we make and sell traditional jewelry. Making custom pieces as needed, with shorter waiting times and less need for keeping stock could transform how the industry’s supply chain works.
Also, it anticipates that the combination of AI and machine learning in jewelry design software will lead to fresh options for making exceptional designs based on data. This means there could be more designs created which are customized to individual choices and market demands.